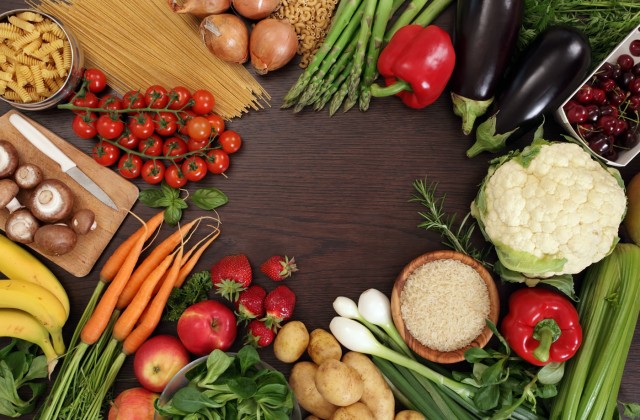
Nutrition is an extremely important part of being healthy and feeling good. The food that we put in our bodies can make us feel great, healthy, and unstoppable–or it can make us feel sick, slow, and lethargic. Since people can have very different dietary needs from one another, nutrition isn’t a one-size-fits-all matter, but there are several tips and facts that apply to everyone.
There are six classes of nutrients that need to be consumed for the body to function properly and to the best of its ability. They are: Carbohydrates, Fats, Protein, Vitamins, Minerals, and Water. Out of these six nutrients, only Fats, Carbs, and Protein provide calories. And despite what the general idea about calories seems to be, they are not bad for you. They are not units of fat, they are Units of Energy. Without a sufficient amount of calories, our bodies can not function properly and we won’t have enough energy to get through the day. Each person has a recommended caloric intake (the amount of calories needed by the body daily) based on their height, weight, age, and activity level. Here’s an online calorie calculator so you can get an estimate of how much you should be eating in a day. The three calorie providing nutrients (fats, carbs, and protein) are called Macronutrients and are a very important part of every person’s diet.
CARBS
There are two different types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. Simple Carbs (also known as simple sugars) usually contain refined sugars and very small amounts of vitamins and minerals. They should be eaten in moderation because they cause spikes in blood sugar levels. While this may not sound like a big deal–if a person’s diet consists of too many simple sugars over a long period of time–it can cause health problems such as Type Two Diabetes, and is also a contributor to weight gain. Simple carbs also breakdown faster and you’ll find yourself feeling hungry much faster. Some examples of simple carbs are table sugar, fruit juices, honey, pop, and jams or jellies. Complex Carbs are much more nutrient dense and filling. They usually contain significant amounts of fiber and do not spike your blood sugar level to the extent that simple carbs do. Some examples of complex carbs are green vegetables, whole grain breads and pastas, oats, potatoes, sweet potatoes, beans, lentils, and brown rice. Carbohydrates are the main energy source used during exercise, brain activity, and the operation of organs. Carbs have roughly 4 calories per gram and should make up about 45-65% of a person’s daily caloric intake.
PROTEIN
Protein makes up our hair, skin, bones, muscles, organs, and every other tissue we have in our bodies. It is used for the growth, repair, and maintenance of these tissues. Protein is made up of strands up amino acids. There are twenty different types of amino acids which can be broken down into two categories: Essential Amino Acids, which we we need to take in from our diet, and Non-essential Amino Acids, which our body produces on its own. A source of protein that has all eleven essential amino acids is called a complete protein. All animal foods like meat, eggs, and fish are complete proteins, but very few vegetarian foods are. It is still possible to get all the necessary protein on a vegetarian or vegan diet, though. It is just very important to get your protein from a wide variety of different foods like soy beans and quinoa (which are both complete proteins) and incomplete proteins like beans, nuts (which are also high in healthy fats), lentils, tofu, seeds, and edamame. Many protein foods are also packed with other nutrients like healthy fats, carbs, and omega-3. The leanest forms of protein are chicken, fish, lean beef, eggs, beans, and legumes. Protein has roughly 4 calories per gram and should make up about 10-35% of a person’s daily caloric intake.
FATS
Fat is an essential nutrient for life. It contributes to brain composition and function, vitamin absorption, cholesterol and hormones, insulation and protection of organs, and hair and skin health. Fat takes longer to digest so it leaves you feeling full longer and it’s also used as an energy source during exercise.
There are four kinds of fats in our foods: saturated fat, polyunsaturated fat, monounsaturated fat, and trans fat. Saturated Fat is the thick, lardy looking kind of fat that is in butter and you can see on bacon and other fatty meats. It will be solid at room temperature and typically stays more solid in the body. This kind of fat is fine in moderation, but if it is consumed in too high of amounts, it can lead to high cholesterol, heart disease, and obesity. It is suggested that only about 10% of our total calories come from saturated fat each day. Monounsaturated Fat is a healthy fat that is found in avocados, olive oils, nuts, and seeds. These fats will be liquid at room temperature and will stay that way in your body. There are considered heart-healthy and anti-inflammatory. Polyunsaturated Fats are where we find our omega-3 and omega-6 healthy fats. Just like monounsaturated fats, poly fats will be liquid at room temperature as well. They can be found in many kinds of fish, like salmon and trout, chia seeds, and many different oils like soybean oil. The last type, Trans Fats, are a completely man-made fat. It is found in processed foods like chips, cake, and donuts because they add to texture and shelf-life. Trans fats are said to raises levels of LDL cholesterol (the bad-for-you kind), and lower HDL cholesterol (the good-for-you kind), which can be very harmful to your heart health. Trans fats are recommended to be very minimal or cut out completely. Overall, fats have roughly 9 calories per gram and should make up about 20-35% of a person’s caloric intake.